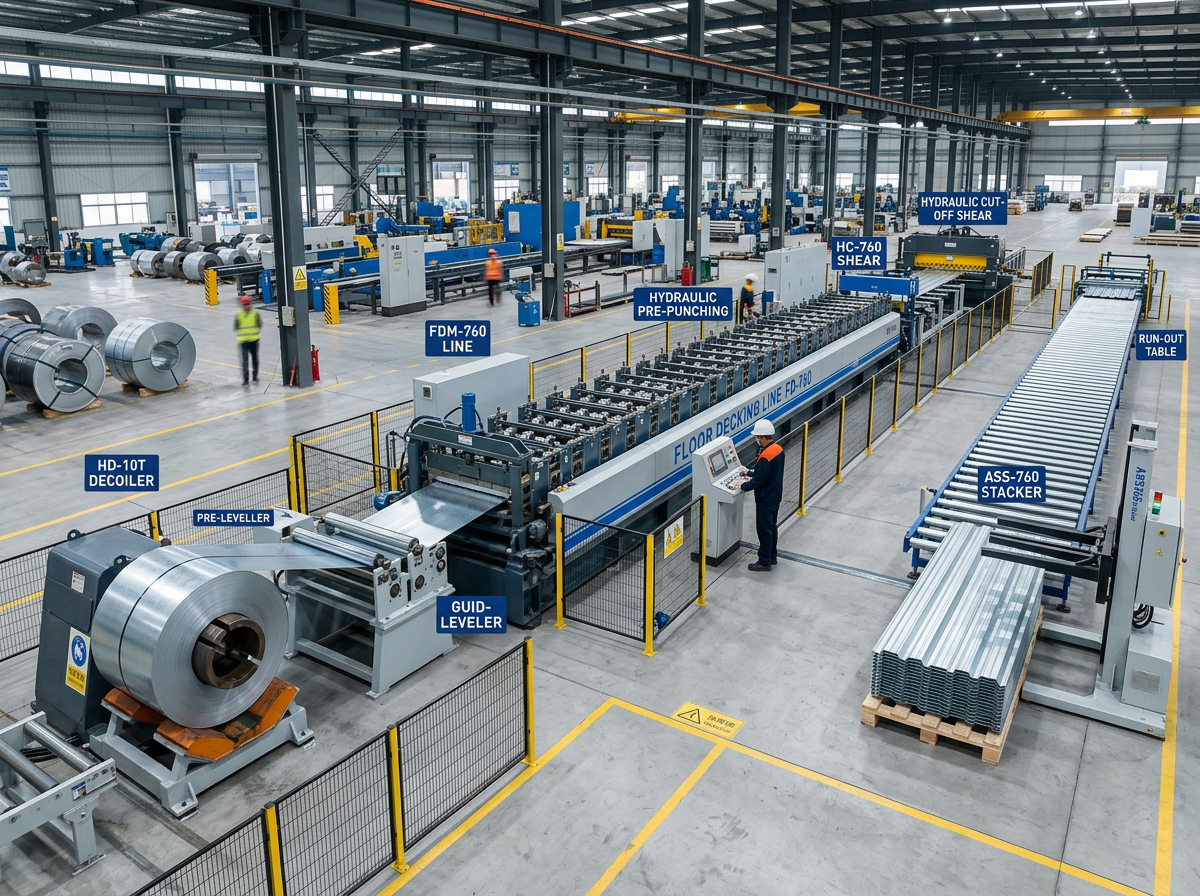
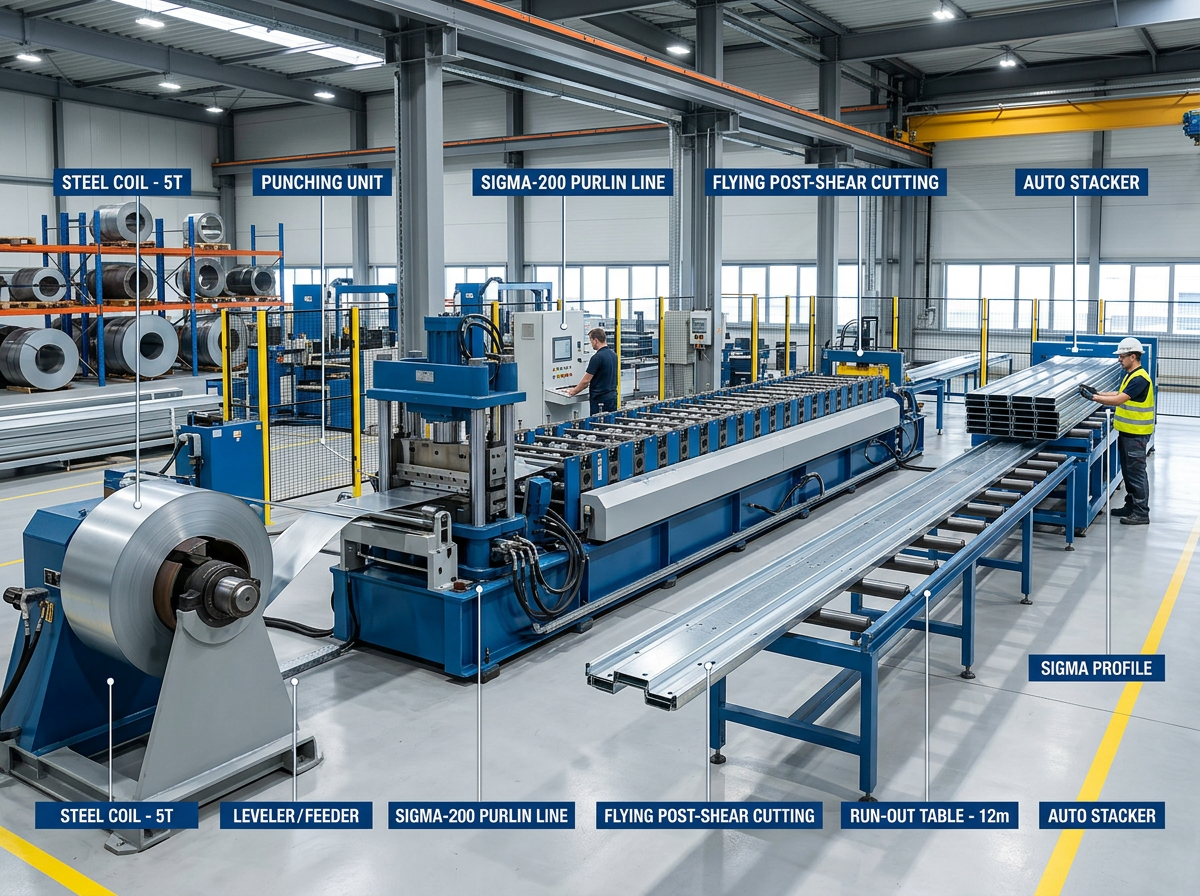
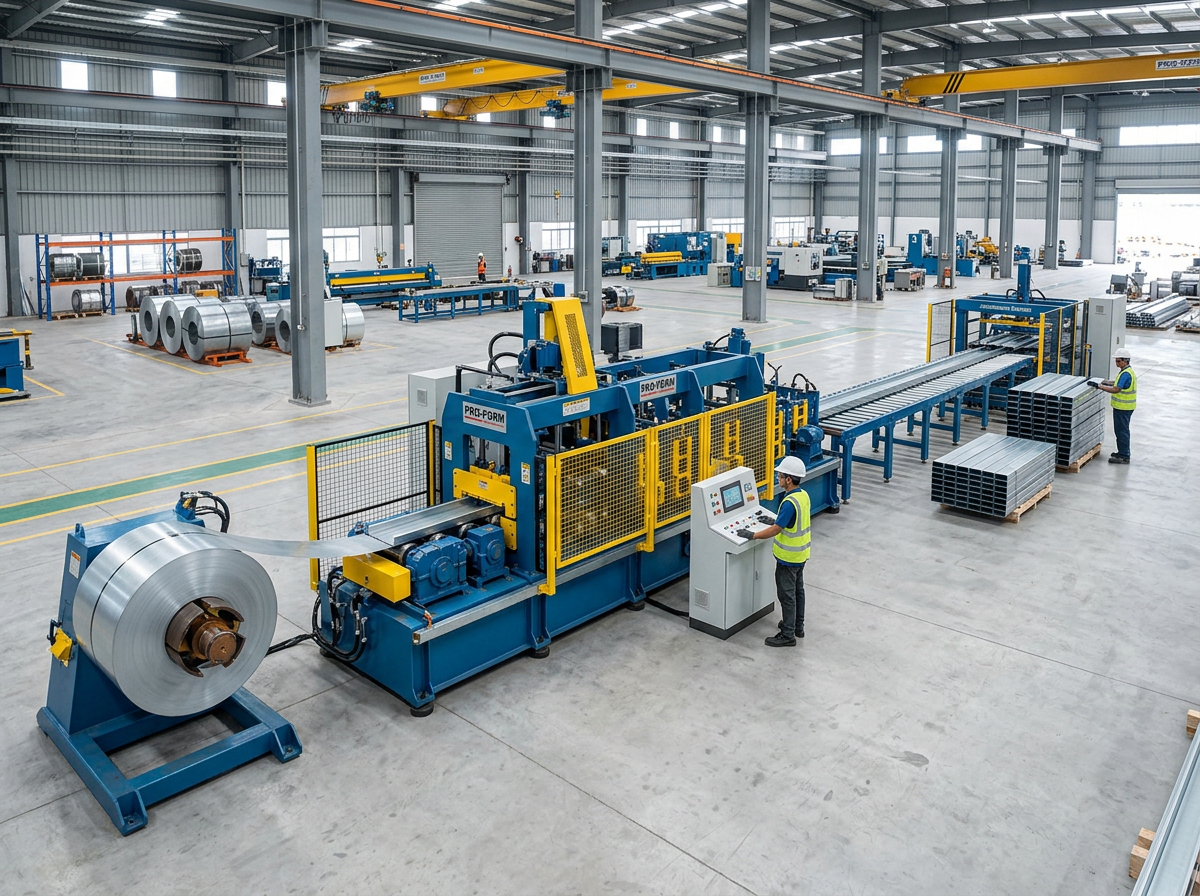
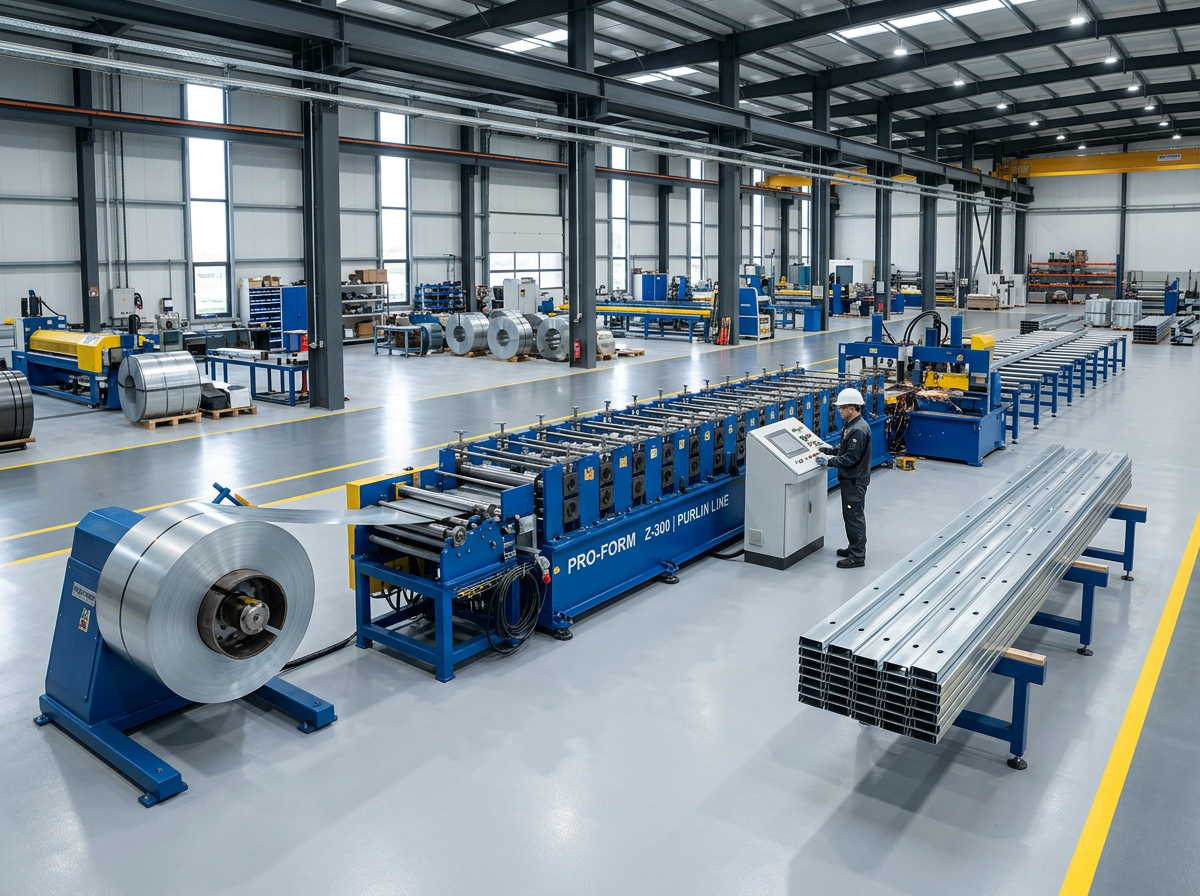
Shelf rack upright roll forming machines enable efficient on-site production of structural steel vertical columns supporting warehouse storage racking systems. This guide provides manufacturers, contractors and building owners detailed technical specifications, configurations, comparisons and considerations when investing in these specialty automated roll forming system solutions.
Introduction to shelf rack upright roll forming machine
Roll formed rack uprights provide unique advantages versus alternatives:
- On-demand manufacturing aligned with deployment schedules
- Inline punching and bracket insertion reduces secondary fabrication
- Low equipment investment for small regional producers
- Agile trailer systems deployable near project site as needed
- Reduces shipping from external rack manufacturer locales
This guide covers key factors evaluating specialty roll forming machines producing structural racking components:
- Working Principle and Process Overview
- Type Comparison – Mobile Trailer vs Factory Systems
- Material, Color and Gauge Capability Ranges
- Forming Speed, Accuracy and Dimension Flexibility
- Integrated Features – Hole Punching, Bracket Insertion
- Supplier Price Bands and Regional Availability
- Installation Requirements and Site Planning
- Operation, Changeovers and Preventative Maintenance
- Pros vs Cons: Roll Formed vs Site Assembled Racks
- FAQs on Building Standards and Seismic Codes
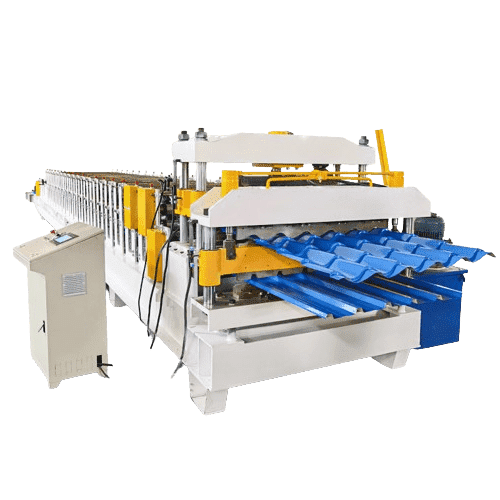
Working Principle of Rack Upright Forming Lines
Roll forming incrementally transforms structural steel coil into C or Z shaped load bearing profiles through a series of roller die bending and calibration stages. Table 1 depicts the typical process steps in sequence:
| # | Station | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Decoiling | Sheet loaded onto powered unwind reel |
| 2 | Feeding | Sheet threaded through initial feed rollers |
| 3 | Forming | Sheet progressively shaped through rolling dies |
| 4 | Punching | Holes stamped for horizontal beam mating |
| 5 | Hardware Insertion | Brackets inserted automatically |
| 6 | Cutoff | Formed columns chopped to length |
| 7 | Evacuation | Finished uprights ejected for collection |
Servo electric motors precisely control piece length, hole spacing, shear blade and hardware insertion synchronization to produce racking with strict dimensional tolerance for easy assembly.
With properly developed Level 2 feeds and speeds integration combined with purpose built rigidity, remarkable innovation flexibility emerges by manipulating optimal variables downstream. Factors including material flow plasticity at focused deforming stress concentrations determined through simulation iteration guide precision recipe configuration on advanced forming lines.
Carefully designed precision preproduction trials combined refined Level 3 verification builds process engineering knowledge for successfully shaping structural shelving previously limited to manual efforts.
Comparing Mobile Trailer vs Factory Upright Machines
Rack upright sections suit repetitive manufacturing in fixed regional plants. However contractors increasingly adopt versatile mobile lines offering logistics agility quick to deploy near erection sites for oversized components avoiding shipping that demand permits or expensive escorts. Table 2 compares capabilities:
| Mobile Trailer System | Fixed Factory System | |
|---|---|---|
| Location Flexibility | Positioned conveniently near project site | Permanent builds limit destination agility |
| Section Length | Up to 20 feet suitable for containers | Up to 40 feet lengths |
| Section Variety | Common profiles standardized | Library of tools for greater variety |
| Process rate | 10 – 25 linear feet per minute | 25 – 45 linear feet per minute |
| Accuracy | +/- 1mm over 8 meter lengths | +/- 0.5mm over 12 meter lengths |
| Computerization | Manual production set up | Fully automated SCADA analytics |
Evaluate tradeoffs like delivery, precision, fast model changeovers and location variables. Modularity suits frequent relocation so temporary lines later upgrade into advanced permanent capabilities while retaining primary roll units capital.
Material, Color and Gauge Capability Ranges
Structural racking uprights require metals that reliably form into high strength cold rolled or hot formed concentric hollow Cross-sections.
Table 3 Shows typical grades and thicknesses:
| Material | Common Gauges |
|---|---|
| Hot Rolled Steel | 3 – 5mm wall thickness |
| Cold Rolled Steel | 1.2 – 4mm wall thickness |
| Stainless Steel | 1 – 2.5mm wall thickness |
| Aluminum | 3 – 4mm wall thickness |
Steel grades S250GD through S550GD galvanized typical based on regional stock availability, cost and rust prevention lifecycle objectives.
Upright roll machines normally form gauges from 0.5 mm steel up through 8 mm plate with increasing gear ratios for heaviest walls that spread tooling stresses over additional vertical rolls.
Evaluate targeted material specifications balancing rated column load capacity, shelving beam mating fitments, fastening methods and budget.
-
 Corrugated Panel Roll Forming Machine
Corrugated Panel Roll Forming Machine -
 Light Gauge Steel Roll Forming Machine
Light Gauge Steel Roll Forming Machine -
 Steel Box Plate Making Roll Forming Machine
Steel Box Plate Making Roll Forming Machine -
 Din Rail Roll Forming Machine
Din Rail Roll Forming Machine -
 Omega Purlin Roll Forming Machine
Omega Purlin Roll Forming Machine -
 CZ Purlin Roll forming machine
CZ Purlin Roll forming machine -
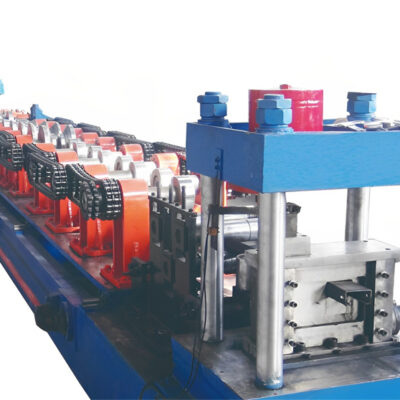 Full automatic C purlin roll forming machine quick-change
Full automatic C purlin roll forming machine quick-change -
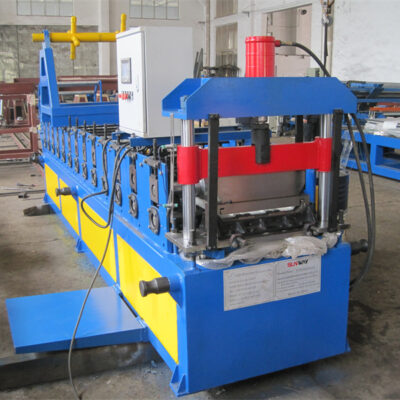 Standing Seam Roof Panel Forming Machine
Standing Seam Roof Panel Forming Machine -
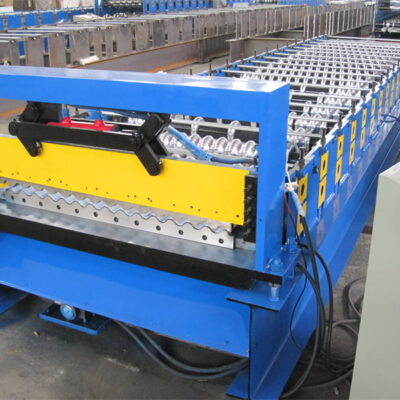 Roof Tile Roll Forming Machine
Roof Tile Roll Forming Machine
Forming Speed, Accuracy and Dimension Flexibility
Depending on profile complexity racking uprights roll form between 10 – 45 linear feet per minute with accuracy and speed relations.
Table 4 indicates normal expectation ranges:
| Low Volume Machine | High Speed Machine | |
|---|---|---|
| Rate | 10 – 20 ft/min | 25 – 45+ ft/min |
| Tolerance | +/- 1.5mm | +/- 1.0mm |
| Stands | 10 – 12 stands | 15 – 22 stands |
| Section Range | 1-2 profiles | 10+ quick change tool sets |
Robust platforms with reinforced frames resist 300 kN of uncoiling force while fast rates demand precision sequencing through subsequent roller dies into finished profiles.
Design flexibility depends on available quick change tooling for depth, flange width, hole patterns and vertical web flatness combinations across common Z, C and L structural shapes. Quantify dimensional expectations when researching equipment capabilities.
Inline Features: Hole Punching & Bracket Inserts
Structural racking requires hardware fitments mating components together so modular enhancements for inline fabrication increase productivity:
Table 5
| Customization | Description |
|---|---|
| Hole Punching | Vertical column holes for beam mating |
| Bracket Insertion | Drop in horizontal beam mating clips |
| Embossing | Decorative logos branded onto surface |
| Markings | Part numbers, serial codes for traceability |
| Safety Warnings | Installed electrical conduit indicators |
Assess specialized requirements like hole patterns during design that increase line efficiency over secondary operations cost burden.
Simple pick and place hardware fits seamlessly. Advanced custom hole patterns may warrant dedicated punching dies that slow set up. Evaluate capability tradeoffs during equipment selection phase once clear on regulatory requirements across global markets.
Supplier Price Bands and Machine Selection
Reputable roll forming manufacturers offer specially engineered upright lines with vast upfront capital costs that demand long term planning.
Table 6 indicates general price ranges:
| Line Configuration | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Basic Manual Trailer System | $60,000 – $125,000 |
| Automated Trailer System | $150,000 – $225,000 |
| Permanent Fixed Factory Mill | $250,000 to $500,000+ |
Pricing depends heavily on degree of automation, accuracy grades, platform ruggedness and flexibility designed into machines to fulfill variety over decades of use. Significant regional cost differences exist between domestic and imported sources.
Carefully project long term business plans when evaluating capitol outlay for balancing current cash constraints versus sustaining consistent production as cyclical order ebbs and flows.
Vendor verification helps navigate tricky durable goods acquisition across global partners with less transparency and legal recourse. Creative requirement interpretation introduces unvetted capability gaps revealed post-payment anchoring equipment. Recouping operational deficiencies proves exponentially costlier over decades of hampered output. The velocity platform intrinsically enables or handicaps future volumes so rigorous due diligence around design mastery and upgrade provisions deserves appropriate weighting when deciding between initial price versus reliable long term capability delivery worth well beyond list value over expected system lifetimes. Disciplined methodical verification is mandatory.
Installation Planning Requirements
Specialized structural rack upright roll forming machinery requires extensive planning to receive expensive multi-ton production lines without foundation or delivery damage.
Table 7 overviews site considerations:
| Factor | Details Checklist |
|---|---|
| Space/Access | Measure door heights/widths ensuring entry clearance. Verify rigging pathway avoiding building obstruction |
| Concrete Foundations | Engineer thick pads preventing machine vibration. Allow underground trenching for site utility access |
| Power Supply | Confirm transformer & distribution to support drives |
| Network Comms | Ethernet cabling for monitoring systems & data pipelines |
| Compressed Air | Clean/dry utility air line for hardware insertion |
| Lighting | Full LED illumination along entire roll line length |
| Cladding | Insulated metal siding for personnel acoustic protection |
| Safety Controls | Guarding, safety mats & infrared beams |
| Logistics | Coordinate truck unloading delivery |
Thorough planning combined with effective site communication prevents delays and additional expenses preparing equipment foundations ahead of production line delivery.
Carefully design machine substrates, electrical loads, compressed air and finishing requirements during initial concept stages rather than reactively altering surroundings trying to install as an afterthought. Responsible preparation streamlines site commissioning and worker training launching new factory capabilities.
Operation, Training and Preventative Maintenance
Specialized racking upright roll forming machinery relies upon orchestrated interaction between automated manufacturing sequences guided through properly calibrated instrumentation synchronizing hundreds of actuations along the entire process chain flow.
Staff roles include:
- Conductor – Directs daily schedule orders while positioning worker skillsets to smoothly execute planned job sequence changeovers between machine A and B activity batches to output pieces effectively without injury or quality violations through oversight.
- Operators – Carefully loads heavy mill coil stock using overhead cranes while monitoring feed alignment preventing sheet tracking distortions through subsequent forming stations. Continually reviews column profile dimensions visually, halting defects before secondary value-add.
- Quality technician – Validates finished geometries using calibrated measurement, assessing upright lengths/hole positioning/hardware insertion alignment against engineering drawings. Flags any out of tolerance conditions for line stoppage, inspecting root cause originating from raw material defects, worn tooling gradual drift, clamp force deviations or software control loop anomalous code execution amplifying over run time.
- Maintenance lead – Sustains equipment integrity through both routine preventative replacement of wear components and break-fix diagnostics pinpointing why functional failures occurred then organizing skilled trades personnel to rapidly correct the system back into capable condition.
- Electrical lead – Masters software, sensors and data analytics including PLC code improvements beyond generic factory settings by tuning servo gains and motion synchronization. Oversees info security and backup integrity while submitting bug captures for external engineering firmware upgrades.
- Tooling specialist – Metrologist able to quantify roll stand alignment geometries down into the micron regime using both contact and noncontact precision measuring devices while providing mechanical support adjusting presses, load cells, parallelism gauging and in house die modifications that further optimize throughput rates or enable accelerated maintenance of worn components before overall equipment losses snowball.
Carefully plan staffing models across these interdisciplinary competencies through combination of internal team development plus leveraging external specialist partners selectively. Budget comprehensive training programs to share best practices between sister facilities while recognizing the inevitable need for tailored operating procedures addressing niche nuances specific to custom lines that responsibly embed hard fought wisdom. Seek experienced consultant guidance establishing detailed standard protocols that elevate safety vigilance across generations of leadership. Recognize the long runway reaching capability maturity over years necessitating unwavering commitment despite front loaded capital investments. Patience, advanced planning and availability of specialized subject matter expertise prevents stunted capability delivery severely handicapping reliability and volume responsiveness.
Pros vs Cons: Roll Formed vs Assembled Racks
Roll formed pallet racking components provide advantages but also limitations over traditional fabricated and assembled alternatives:
Table 8
| Parameter | Roll Formed | Site Assembled |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Very fast installation after forming | Slower piece-by-piece manual buildup |
| Efficiency | Automated process with less touch labor overall | Highly labor intensive |
| Alignment | Superior hole alignment reliability | Risk of mating connection gaps |
| Strength | Full thickness interlocks load path | Individual sheet joint articulations |
| Equipment Cost | Major one time investment | Lower – uses existing tools |
Other considerations:
- Roll formed achieves lengths impossible to handle lifting manually
- Controls ensure precise consistency preventing cascading rework
- Low long term maintenance over shelving lifetime
- Easier integration of safety placards during forming
- Damage risks during shipping and concrete anchor installation
Evaluating productivity, quality and costs determines optimal techniques for manufacturing steel storage shelving components at sustainable volumes. One time equipment acquisition costs amortize over future annual production capacity surpassing variable manual fabrication reliant upon inconsistent labor availability. When responsibly engineered to strict quality standards, automated machines increase output predictability otherwise unattainable relying solely upon workmanship vulnerability prone to capability gaps without standardized tools enforcing disciplined guardrails. Upon recognizing the exponential accuracy loss introduced beyond certain unmanageable length thresholds, sensible dialogue around physical limitation factors helps discover the pragmatic lean investment point balancing production methodology between augmented mechanical processes against solely depending upon specialist subcontractor skill availability. Often selectively blending approaches strikes the right balance.

FAQs
Table 9 – Buyer Queries
| FAQ | Answer |
|---|---|
| What load rating should I expect per shelf? | 50 lbs to 200 lbs dynamic medium duty rating typical for roll formed racking |
| Can I get custom powder coated finishes? | Yes integrates easily with in-line pretreatment systems |
| What beam adjustment range is typical? | 50mm leveling bolt slots common for rebar mat settling |
| Does pricing include hardware kits? | No – unique per distributor preference on bolt types |
| What prevents shelving collapse accidents? | Strict quality adherence combined with mandatory site audits checking proper assembly |
Table 10 – Technical Performance Questions
| FAQ | Answer |
|---|---|
| How is rated capacity validated? | Per engineer guidance, assembled frames undergo incremental overload simulation to factors of safety |
| How do I check for damage during relocation? | Document original install photos including concrete floor marks to baseline move comparisons |
| What quality standards apply? | RMI MH16.1 guidelines govern US manufacturing while local equivalents apply for export destinations |
| Should roll formed racks be anchored? | Yes concrete anchors mandatory in high seismic zones per IBC 2018 |
| How frequently should I audit installations? | Annual inspections checking for loose components, beam creep, plumbness deviations |




